A product is a combination of services that you provide to a customer for a price. For example, you decide to sell calling cards with 10 cents/minute calls to the Czech Republic for calls to a local access number in New York, and 15 cents/minute + 50-cent connection fee for calls to a toll-free line. In this case, your product will include two types of service:
access via the local New York number, and
access via the toll-free line, with price parameters associated with each service.
Rating entry is the main component of a product definition. It specifies where your customers are allowed to use a service and how they should be charged for it. Rating entry allows you to specify the following parameters which define an access point:
The type of service provided.
The node on which the service is used. What exactly does “node” mean in this context? If, for example, a customer calls to gateway A, enters his PIN, and makes an outgoing call which is terminated on gateway B, is he using a service on node A, node B, or both? The correct answer is that the service is regarded as having been provided at the point where authorization was performed. In this example, since PIN authorization is performed on node A, it is node A which must be listed in the rating entry.
A tariff with a complete set of rates. Thus it should include every possible destination allowed by your customers’ service plan (e.g. in the case of a telephony service, every destination to which you want to let them call).
Identification of the access code (method) on that node. This parameter allows you to use different rate plans for the same service. For example, you may choose a rate plan according to the PSTN access number (local or toll-free) that the customer has dialed. Or you may use different rate plans for outgoing, incoming and forwarded calls in your IP calls service. (While for services such as prepaid cards the access code is a number, for other services any string may be used, so long as it is one provided by the application handling the call).
Originating line information (this is applicable only to the voice call service). You can separate rating entries based on originating line information (e.g. whether the call was made from a home phone or a pay phone). Make sure your telecom provider supplies you with this information in the call setup.
A service consumption policy for suspended customers. For example, you may want to allow such customers to continue receiving incoming calls (since they are free.)
The rate match mode that allows you to rate calls based either on their destination or on the caller’s number.

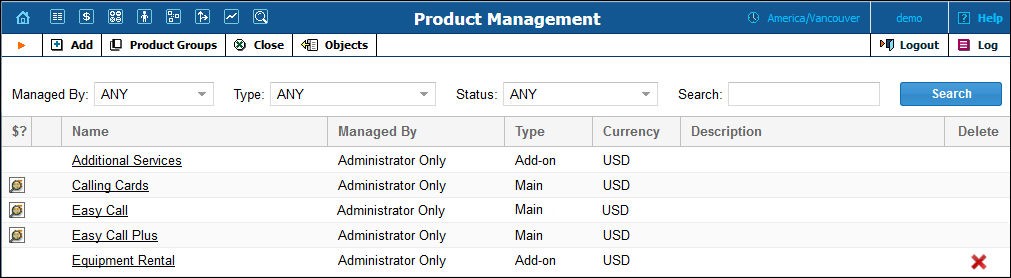
On the Product Management page, the user may view the list of all registered products. The list provides the following information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
$
|
Click the |
Name |
The logical designation of the product. |
Managed By |
|
Type |
The product type can be the following:
Add-on products have precedence over the main product, so no matter what is defined within the main product, it will be overridden by settings defined within add-on products (this applies only to the options that are supplied with add-on products). In order to differentiate the add-on products there is also a “precedence level” parameter for each add-on product. If there are more than one add-on products assigned to an account they will be sorted according to the specified precedence level. |
Currency |
The currency in which the product will be maintained. |
Description |
Product description. |
Delete |
Click the |
To add a new product to the system,
click  Add to
go to the Add Product page.
Add to
go to the Add Product page.
Existing product can be edited by clicking on the product's name in the list.