 Policies are
applied separately to both parties (caller and called) participating in
the call.
Policies are
applied separately to both parties (caller and called) participating in
the call.The telecommunication industry is growing rapidly, with new technologies and devices being introduced into the market every year. Networks have become more flexible and customers have become more demanding about the services that they subscribe to. Under these conditions, it is essential not only to continually offer new services and products and therefore keep up with market demand, but also to do this in the most qualitative and flexible manner. This is what PortaBilling enables you to do!
The Service Policies feature allows you to fine-tune your services based on your network peculiarities, vendors’ opportunities and customers’ demands. It facilitates the configuration of static options for multiple accounts (so it is not necessary to configure values for each account separately), thus establishing common policies for groups of accounts. It also allows you to separate the technical configuration of specific options (usually made by technical staff) from account management.
When a new policy is created it does not have any attributes defined (all available attributes are shown in grey). To define an attribute you should specify its value.
Service policies can be either be:
 Policies are
applied separately to both parties (caller and called) participating in
the call.
Policies are
applied separately to both parties (caller and called) participating in
the call.
The service policy has the ability to match dynamically when the Match Pattern is specified. For the calling party, PortaSIP extracts the User-Agent header from the incoming INVITE request (e.g. “Linksys/SPA941-5.1.8”) and matches it against all of the dynamic policies. If more than one policy matches, the one with the highest Match Priority is used.
For the called party, the procedure is quite similar. The only difference is that the User-Agent header of a called UA is taken from its registration information.
More than one service policy can be considered while the call is being established so it is important to know how different service policies correlate with each other and how that affects the call.
The final set of attributes applied to each party is derived from service policies assigned at different levels (a dynamically matched policy is also considered.)
What happens if there is a contradiction in service policies? For example, if a dynamically matched service policy has the keep_alive_interval attribute set to 60 seconds, another service policy assigned to a called party has its attribute value set to 120 seconds and the third service policy assigned to a connection has its attribute set to 90 seconds?
Several simultaneously applied service policies will function according to the precedence of defined attributes that are exact matches:
There is also an attribute-specific prevalence among the service features assigned to both caller and called accounts:
The codec_order_list attribute is taken from the caller’s account (called account’s attribute is ignored).
The “header” attributes (out_hdr_pai, out_hdr_rpid, out_hdr_history, out_hdr_diversion) defined for a called account will take precedence over the ones defined for a caller account.
The keep_alive_interval attributes are individually defined for the caller and called parties, so there is no predominance between them. Therefore the value for the caller party is taken either from the dynamically matched service policy or the one assigned to his account. The value for a called party is taken either from the dynamically matched service policy in case the called party is one of your accounts or the service policy assigned to the connection.
Note that service policy attributes that have been statically assigned to an account receive the highest priority.
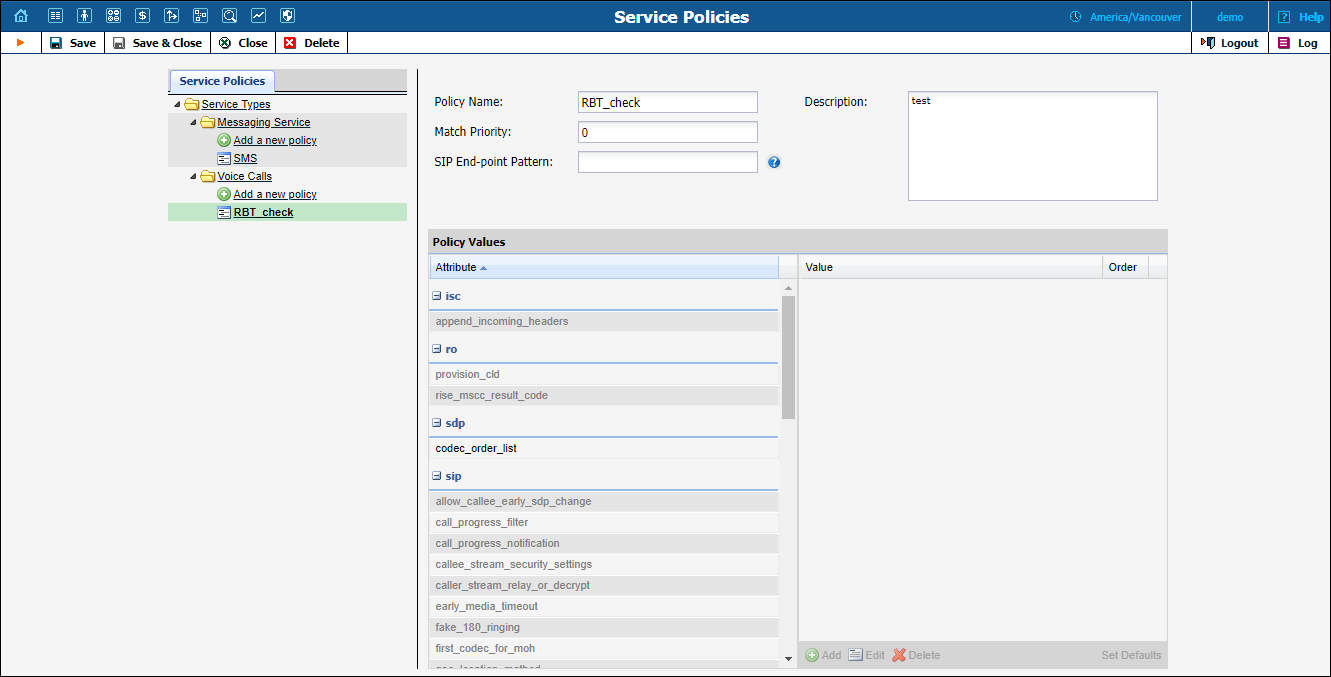
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Policy Name |
This is the logical name of the service policy object. |
Match Priority |
This is only used for policies that match dynamically. If more than one service policy corresponds with the caller’s user agent name then the one with the highest priority will be used. |
SIP End-point Pattern |
If this field is not empty the service policy is considered to be dynamically matched and will be attempted for every new call initiated by internal accounts.
This field can contain a full user agent name (e.g. “Linksys/SPA941-5.1.8”) or a comma separated list of patterns (e.g. “Cisco%, Sipura%, Grandstream%”).
NOTE: If the policy is statically assigned to an account, it will always be applied (in spite of the match pattern). |
Description |
This is a short description of the service policy. |
NOTE: You can define custom attributes to satisfy your specific requirements but a description of this lies beyond the scope of this document due to its specific characteristics.
| Attribute | Applied to | Description |
|---|---|---|
ics |
This section describes service policy attributes that define the rules of interoperation between PortaSIP® and the IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem). | |
append_incoming_headers
|
called party | This attribute defines that the call is intended for the mobile network and that PortaSIP® must route the call to the IMS core.
It also defines that PortaSIP® must preserve the ODI (Original Dialog Identifier) of the call when routing it to the IMS. The IMS uses the ODI to match messages to / from PortaSIP® into a single SIP dialog.
Note that the account must not be registered on an IP device. Otherwise, the account registration will override the service policy settings and PortaSwitch® will attempt to terminate the call on a VoIP network.
This attribute is ignored for the calling party. |
ro |
This section describes service policy attributes that allow you to adjust the communication between PortaBilling® and IMS for VoLTE service provisioning. | |
provision_cld |
connection | This attribute allows you to customize the Diameter response sent by PortaBilling® so it includes the Called-Party-Address attribute. The Called-Party-Address is a callee’s ID with translation rules applied. The default value for this attribute is No since the Called-Party-Address is not required by the majority of gateways.
If your Public data network Gateway (PGW) requires the Called-Party-Address to be included in the response, set the value to Yes. |
rise_mscc_result_code |
connection | Most gateways connect or terminate calls based on the Result-Code value that is set within the MSCC (Multiple-Services-Credit-Control) AVP. However, some gateways (e. g Huawei ATS 9900) require that the result code be set for the Result-Code AVP.
This attribute allows you to customize the Diameter CCA (Credit-Control-Answer) sent by PortaBilling® so that it copies the Result-Code value from the MSCC AVP and sets it as the Result-Code AVP.
The default value for this attribute is No. To enable this option set it to Yes. |
sdp |
This section describes service policy attributes that deal with the SPD (Session Description Protocol) and thus define the rules of how a multimedia session can be set up. | |
codec_order_list |
calling party | Allows the sorting of the codecs list that is configured for a routing plan.
When this attribute is defined, codecs received in the initial INVITE message will be reordered according to the list specified here.
For example, calls to carrier X are sent using the G.711 codec, but you want to send calls using the G.729 codec. You also want to retain the option of sending calls using G.711 in case G.729 is not available.
This attribute is taken from the service policy applied to the calling party; it is ignored if defined for the called party.
Note that this attribute is applicable only when the Enforce codec order option is enabled for the connection on the Routing Filter tab. |
sip |
This section describes the service policy attributes that define signaling during call setup for a particular UA type. | |
always_reliable_1xx |
dynamic service policy | This attribute facilitates early dialog processing with UAs that send malformed provisioning responses to requests with the Supported: 100rel SIP header. That helps prevent stuck sessions with locked funds and allows further service usage.
When this attribute is enabled in dynamically matched service policy, PortaSIP® treats such unreliable responses with SDP as a confirmed answer and proceeds with call processing. Otherwise, PortaSIP® generates the 500 error code and the call is not established. |
allow_callee_early_ sdp_change |
called party | This attribute allows one-way audio issues caused by SDP changes during call setup to be dealt with successfully.
Possible options are:
|
call_progress_filter |
calling / called party, connection | Controls the re-sending progress of early media for both participants of a call.
If this attribute is defined for both calling and called party, the calling party’s options have higher priority and override the options defined for the called party. |
call_progress_ notification |
calling party, connection | Initiates Ring Back Tone generation instead of sending 18x SIP signaling for a call-originating party.
This attribute is ignored for the called party.
Possible options are:
|
callee_stream_ security_settings |
called party | Defines the type of media encryption for the called party during the call.
Possible values are:
|
caller_stream_ relay_or_decrypt |
calling party | Defines the types of media encryption and processing for the calling party during the call.
Possible values are:
|
early_media_ timeout |
called party, connection | This attribute defines a duration in which PortaSwitch® waits for RTP media packets upon receiving an 18x Ringing response with the SDP from the called party. If they are not received within the predefined timeout, PortaSwitch® generates its own ring-back tone for the caller. |
fake_180_ringing |
calling party | If set to Yes, PortaSwitch® sends a ‘180 Ringing’ SIP response to the caller immediately after the originating outgoing INVITE request. If set to No, PortaSwitch® waits for the ‘180 Ringing’ SIP response to be sent by the UA of the called party. |
first_codec_for_moh |
calling / called party | When one party (e.g. a caller) is put on hold during a call,
their UAs re-negotiate the session. In some cases, a caller’s
UA may request a different codec from the one initially negotiated
for media streaming.
This attribute defines which codes will be used to play the music on hold for the party on hold.
|
force_sip_proxy |
called party | If set to Yes, PortaSIP® always involves the SIP proxy in the call, even in the case of call termination to a gateway or SIP-URI. This attribute helps deal with NAT issues. |
force_route_through_dsbc |
connection types:
|
This instructs PortaSIP® to send outgoing call initiation requests
to the dispatching SBC. The dispatching SBC then sends the request
to the destination.
This type of flow keeps the network configuration for customer IP PBXs and gateways hidden behind NAT unchanged as they send and receive requests from the same IP address. Sending outgoing requests via the dispatching SBC imposes additional load to it. Therefore, assign the service policy to connections only when required. |
geo_location_method |
connection, call handling rule | This attribute instructs PortaSIP® to handle the “P-Access-Network-Info”
SIP header and obtain information about the operator who handles
the call.
To make PortaSIP® check the header in the incoming INVITE request for a wholesale customer, the policy must be assigned to the corresponding call handling rule. To make PortaSIP® send the header in the outgoing INVITE request, the policy must be assigned to the vendor connection. |
gw_longpound_ event |
calling party | When a user makes a call to an IVR application (e.g. prepaid card, callback pass-through IVR), PortaSIP releases media upon connection. When a user dials a long pound key (##), this event is passed to PortaSIP® in the SIP INFO message.
PortaSIP® uses this input to disconnect the user’s outgoing call leg and continues regular IVR flow processing for the user.
The following options are possible:
This attribute is used for calls that originated on the Sonus PSTN gateway and works in conjunction with the Release Media Upon Connection option enabled for the IVR application. It is applied to the calling party and is ignored for the party called. |
hunt_stop_codes |
outgoing connection | This attribute is used to adjust call routing for the calling party if:
Recommended values:
When a connection is tried and PortaSIP® receives a response with a code that matches the one defined, further routing for the call is stopped. |
initial_negotiation_ codecs |
calling / called party | Defines the codecs list for an SDP generated by PortaSIP® during call pickup if both parties start their calls with a late offer-answer model. If this attribute is defined both for the calling and called parties, common codecs are used. If the list is empty, such pickups are impossible.
Select codecs from the list. |
initial_sdp_on_ transfer |
calling party, call handling rules | This option forces the codec list sent to the transfer target to be the same as the initial codec list from the transferee.
Without this option, the INVITE to the transfer target will contain the last received codec list that was negotiated with the transferee. |
keep_alive_interval |
called and / or calling party | Defines the keep-alive (re-INVITE) interval in seconds for the party (calling or called) that has this option set. Dialing 0 disables keep-alives for the corresponding party. |
no_voice_rejects |
dynamic service policy | This option defines how PortaSIP® responds to a calling party in case of an unauthorized incoming call (e.g. the party called does not exist).
When enabled within the dynamic service policy, PortaSIP® operates as follows, depending upon the option value:
|
old_uri_combining_ for_aor |
called party within dynamically matched service policy, connection | If set to Yes, PortaSIP® will place the dialed number (CLD) both in the Request-URI (RURI) and To headers in the outgoing INVITE request. If set to No, the dialed number (CLD) will be placed in the To header only in the outgoing INVITE request.
This attribute can be used in the following scenarios:
|
on_hold_media_ direction |
connection | This attribute defines the media stream direction when a call is on hold between PortaSIP® and an IP device. NOTE: The on_hold_media_direction attribute defines the media stream direction only if it is sent through the RTP proxy. Select one of the available modes:
|
onjoin_renegotiation_ delay |
calling / called party | When a user picks up a call, PortaSIP® starts the session re-negotiation and sends the re-INVITE requests to a vendor. If for some reason the vendor cannot process the re-INVITE request while the previous SIP dialog is still in process (ACK is not yet received), this service policy attribute defines the delay in milliseconds for the re-INVITE sending by PortaSIP®.
This attribute may help fix one-way audio issued during call pickups and other re-INVITE issues. Both calling and called party options are checked; the greater one is used. |
passthrough_headers |
calling party | Use this attribute to configure which headers B2BUA must let through.
For example, B2BUA strips the Alert-Info header that provides an alternative ring tone for the UA from the incoming request because it may introduce the risk of exposing a callee to dubious content if someone were to exploit the URI contained within.
However, if you are sure that the origin of its content is not questionable you may use this header, having defined it for this attribute.
PortaSIP® will accept all the headers listed in this attribute and forward them on to vendors. |
remote_address_ sip_field |
call handling rule | Defines the SIP header that PortaSIP® must get the remote IP from. |
sdp_cline_mode |
calling / called party, which receives SDP | Defines how to deal with c-line in outgoing SDP.
The following values are available:
|
sdp_ptime_remove |
calling / called party, which receives SDP | Ptime is the SDP attribute that defines the duration of the media stream in milliseconds for a RTP package.
This attribute instructs PortaSIP® to remove ptime from SDP messages in case a legacy IP device cannot process it.
Possible options are:
|
sticky_1xx_sdp |
calling party, ignored for the called party | When enabled, B2BUA registers the first SDP received in an 18x SIP response from the callee and sends it to all resulting 18x SIP responses sent to the caller. This is required in those rare cases when a caller UA violates the RFC3261 and after receiving the first 183 SIP response, is unable to process the resulting provision SIP responses (180, 183, etc.) without an SDP. A Service Policy with this attribute must be applied to the caller.
Possible options are:
|
transfer_caller_cli_header |
calling party initiating a blind transfer | This option specifies the header that is used by PortaSIP to get the CLI for caller authentication. It is only used for blind transfer scenarios. The header should be specified in the REFER request. |
transfer_progress |
calling / called party initiating transfer | Triggers Ring Back Tone generation on 18x SIP signaling during Blind Transfer. Transferor’s option is applied.
Possible values are:
Early media (if sent by the transfer target) is relayed. |
sip.identity |
This section describes service policy attributes that define the outgoing identity. | |
out_hdr_contact |
called party, connection | Specifies which value must be used for the username part of the URL in the contact SIP header of the outgoing INVITE request.
The following values are available:
|
out_hdr_diversion |
called party, connection; ignored for the calling party | Adds the Diversion SIP header to the outgoing INVITE request and specifies the value to be used for the username part of the header’s URL. This header will be added only if the call is being forwarded and will be ignored if defined for the calling party.
The attribute can have the following value:
Disable this attribute within the service policy to skip generating Diversion SIP headers. |
out_hdr_history |
called party, connection; ignored for the calling party | Adds the History-Info SIP header to the outgoing INVITE request and specifies the value to be used for the username part of the header’s URL. This header will be added only if the call is being forwarded and will be ignored if defined for the calling party.
The following values are available:
|
out_hdr_pai |
called party, connection; ignored for the calling party | Adds the P-Asserted-Identity SIP header to the outgoing INVITE request and specifies the value to be used for the username part of the header’s URL.
The following values are available:
|
out_hdr_rpid |
called party, connection; ignored for the calling party | Adds the Remote-Party-ID SIP header to the outgoing INVITE request and specifies the value to be used for the username part of the header’s URL.
The following values are available:
|
outgoing_headers_trusted |
called party, connection; ignored for the calling party | The outgoing_headers_trusted attribute determines whether to include one or both of these headers in a request sent to trusted remote connections.
New attributes specify whether the p-asserted-identity (pai) and remote-party-id (rpid) headers are included in outgoing INVITE requests.
Privacy headers are used when, for example, a caller’s identity must be hidden from a called party, but a vendor still requests this information. In this case, identity information can be included in the privacy header, which indicates that the caller’s info must be withheld from the called party.
Different vendors require and can properly process different privacy headers. Thus, being able to specify which privacy header to send to trusted / untrusted vendors gives you the ability to satisfy both an end user’s request for anonymity and a vendor’s request for identity data.
|
udptl |
This section describes the service policy attributes that deal with UDPTL (User Datagram Protocol Transport Level) and thus define the rules of how to set up fax message transmission via the T.38 protocol. | |
t38_fax_max_datagram |
Dynamically matched service policy | The maximum size (in bytes) of data accepted by PortaSIP® within
the UDPTL packet.
The default value is 849 bytes. Increase this value if data loss occurs during fax reception. |
t38_fax_udp_ec |
Dynamically matched service policy | Fax error correction scheme. This is used to detect and correct errors in fax page data during reception (e.g. if data is missing or has been altered during transmission).
Possible options are:
|
voice.location |
This section describes the service policy attributes that define the caller location in case of incoming calls. | |
primary_location |
incoming connection | Contains the caller location information that is conveyed by
the vendor in the “P-Access-Network-Info” SIP header to comply
with EU regulations.
The attribute value must be defined in the fr.GSTNR1R2C1C1C3C4C5XX format, where:
|
Service policies for Messaging services contain a set of parameters that define how PortaSwitch® subsystems must operate to perform message exchange between end points.
Similar to the Voice calls service, service policies for messaging can either be or be matched dynamically,
The attributes defined in the dynamic service policy (i.e. transport protocol, routing and billing parameters) are used for message processing and delivery (both SMS and instant messages). The static service policies contain attributes specific to a particular SMS vendor.
| Attribute | Applied to | Description |
|---|---|---|
audiocodes.cmms |
This section describes the service policy attributes applicable to users provisioned in the AudioCodes CMMS server. | |
push_events |
product | This attribute enables administrators to control messaging service availability for accounts provisioned in AudioCodes.
When enabled, PortaBilling® sends notification to the AudioCodes CMMS server when a user’s service wallet is empty and their messaging service is suspended. Once a user tops up the service wallet, their messaging service is resumed. |
msg |
This section describes service policy attributes that define message processing and delivery. | |
billing_unit_size |
domain service policy | Defines the message length limit. Long messages will consist
of several. It is used to calculate the number of ‘billing units’
in longer messages.
The message length to be charged as a single message. Long messages are charged for the number of messages they consist of. For example, a message length is defined as 60 chars. A user sends a message that has 150 chars and is therefore charged for 3 messages (3*60). If this attribute is not defined, the user will be charged for a single message, regardless of its length. |
bind_as |
connection | Defines the mode of connection to the server which determines reception and messages sent:
|
dest_addr_npi |
connection | Numbering Plan Indicator for destination SME. |
dest_addr_ton |
connection | Type of number for destination. The following types are available:
|
external_routing |
domain service policy | If enabled, PortaBilling® will return the routing list for message delivery in the authorization response so that PortaSIP® delivers it to off-net vendors.
If disabled, message will be delivered within the network.
Works in conjunction with the local_lookup option. |
heartbeat_interval |
connection | Defines the interval (in seconds) during which ENQUIRE_LINK requests are sent to verify the connection. The default, zero, means no requests will be sent. |
incoming_aaa |
domain service policy | Enables / disables authorization and billing for incoming messages. This will be supported in future releases. |
local_lookup |
domain service policy | If set to Yes, PortaBilling® will check whether
the destination number belongs to one of the accounts within the
network.
If set to No, PortaBilling® will match the destination number with rates from the tariffs. |
outgoing_aaa |
domain service policy | Enables / disables sending accounting requests to PortaBilling®
for outgoing messages.
If it is disabled, IMGate performs authentication only and does not send the accounting request to PortaBilling®. |
reconnect_interval |
connection | The reconnect interval for an outgoing SMPP connection in case of a connection failure. |
registered_delivery |
connection | Numbering Plan Indicator for the SME (Short Message Entity) address where the message originated from.
The possible values are:
|
reject_error_codes |
connection | These are the error codes from your vendor that prevent SMS messages from being resent. Specify the error codes in a hexadecimal format (e.g. 00000058, 58, 0x58). |
source_addr_npi |
connection | Numbering Plan Indicator for the SME (Short Message Entity) address where the message originated from.
The following indicators are available:
|
source_addr_ton |
connection | Type of number for source address SME.
The following types are available:
|
system_type |
connection | This attribute categorizes the type of External Short Message Entity (ESME) system that is binding to the SMSC and requests binding it as a receiver.
Specification of the system_type is optional - some SMSCs may not require ESMEs to provide this detail. |
transport_protocol |
domain service policy | Defines the transport protocol that will be used to deliver the message to the recipient (the default value is set to SIP).
The following protocols are available:
|
userpart_e164_ translation |
domain service policy | If set to Yes, PortaBilling® will use the dialing rules for a phone number translation. |
qualution |
This section describes service policy attributes that define message processing and delivery. | |
push_events |
product | This attribute enables administrators to notify end users about their volume discount plan usage via Qualution in real-time. |
ro |
This section describes service policy attributes that allow you to adjust the communication between PortaBilling® and IMS for VoLTE service provisioning. | |
ro.rise_mscc_result_code |
Most gateways deliver messages based on the Result-Code value that is set within the MSCC (Multiple-Services-Credit-Control) AVP. However, some gateways (e. g Huawei ATS 9900) require that the result code be set for the Result-Code AVP.
This attribute allows you to customize the Diameter CCA (Credit-Control-Answer) sent by PortaBilling® so that it copies the Result-Code value from the MSCC AVP and sets it as the Result-Code AVP.
The default value for this attribute is No. To enable this option set it to Yes. |