
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Login |
The new user ID to be used at login and elsewhere throughout the system. |
Password |
The password for this login. A secure and hard-to-guess password may be automatically generated by pressing the “Auto” button. |
Access Level |
The privileges or role associated with this user. See the Access Levels section for more information. |
Allow login from |
You can ensure that access to the PortaBilling® administrative web interface only occurs from physical locations that you define. For example, you can specify IP addresses that belong to your network. If a user tries to log in from outside your network, PortaBilling® denies that access and the user cannot log in.
The following formats can be used to permit access from specific IP addresses or networks:
You can enter multiple definitions, with each starting from a new line and ending with semicolon. |
API token access |
You should use tokens instead of standard login-password pairs for authenticating your applications integrated with PortaBilling® via API. |
API authentication token |
Input the combination from this field into your application and remove the password from it (the AuthInfoStructure and LoginRequest API structures have the token property). |
Time Zone |
The time zone in which this user will be operating. |
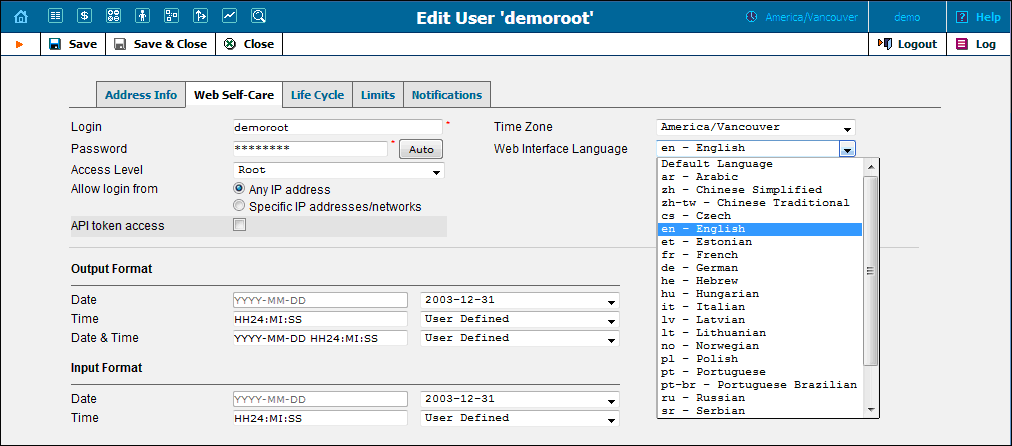
Web Interface Language |
The language to be used on the administrator interface for this user. |
Currently, in addition to English as the main language, the PortaBilling® administrative interface is available in the following languages:
Translations are continually maintained and improved upon by the community of PortaOne customers. New languages may easily be added upon request; please contact PortaOne support to obtain the .xml template files if you would like to make and submit a translation.
Every user of the system (administrator user, account, customer, vendor, customer care administrator) can choose the language of the administrative web interface for his session. This does not, of course, affect other users; thus user John can work with the system using English as his interface language, while user Jane can make use of Chinese simplified as her language.